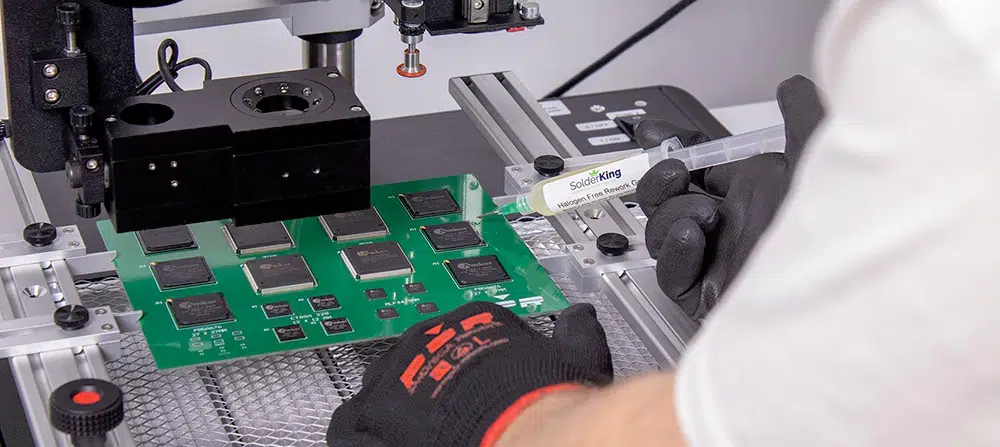
In the intricate world of electronics manufacturing and repair, Ball Grid Array (BGA) components pose unique challenges due to their densely packed array of solder balls underneath the component. These components are prevalent in modern electronics, offering advantages like smaller size, better performance, and enhanced thermal properties. However, when these components fail or need modification, specialized equipment known as BGA rework station becomes indispensable.

What is BGA reworking?
BGA reworking refers to the process of repairing or modifying Ball Grid Array (BGA) components on printed circuit boards (PCBs). BGAs are a type of surface-mount packaging used extensively in modern electronics due to their compact size, high pin count, and superior electrical and thermal performance. However, when a BGA component becomes faulty, damaged, or needs to be upgraded, reworking becomes necessary.
Tools and Equipment Used:
BGA Rework Station: Specialized equipment designed for precise heating, alignment, and soldering of BGA components.
Hot Air Rework Tools: Used for localized heating during component removal and soldering.
Soldering Irons and Stations: For touch-up soldering and fine-detail work.
Optical Inspection Systems: Magnification tools and cameras for inspecting PCBs and ensuring accurate component placement.
What is a BGA Rework Station?
A BGA rework station is a sophisticated piece of equipment designed specifically to remove, replace, and rework BGA components on printed circuit boards (PCBs). It incorporates precise control over temperature, airflow, and alignment, crucial for handling the delicate soldering processes associated with BGAs.
What are the components of a BGA rework station ?
1. Heating System: BGA rework station features heating elements such as infrared heaters, hot air jets, or even lasers, depending on the model and application. These systems deliver controlled heat to the BGA component, melting the solder underneath without damaging the board or nearby components.
2. Optical Alignment Systems: To accurately position the BGA component during rework, advanced stations include optical alignment systems. These systems use cameras and microscopes to ensure proper alignment of the component with the PCB pads, critical for achieving reliable solder joints.
3. Temperature Control: Precise temperature control is essential to prevent thermal damage to sensitive components and the PCB itself. High-quality rework stations offer programmable temperature profiles and real-time monitoring to maintain consistency and reliability throughout the rework process.
4. Vacuum Handling Tools: Removing a BGA component requires careful extraction of molten solder balls. Vacuum handling tools integrated into rework stations efficiently lift the component from the board once the solder has melted, minimizing mechanical stress on the PCB.
5. Software Control: Many modern BGA rework stations come with intuitive software interfaces that allow technicians to set up and monitor rework parameters, store profiles for different components, and ensure repeatability in the rework process.
What is the use of BGA rework station?
1. Repair and Refurbishment: BGA rework station is extensively used in electronics repair centers and manufacturing facilities to replace faulty BGA components without scrapping entire PCB assemblies. This capability reduces repair costs and extends the life of electronic devices.
2. Prototype Development: During the prototype stage of electronic product development, BGA rework station enables engineers to modify designs quickly and validate new components or configurations without the need for costly PCB redesigns.
3. Component Upgrades: As technology advances, older BGA components may need to be upgraded to newer versions with improved performance or features. Rework stations facilitate this process by safely removing obsolete components and installing new ones.
What is the advantage of BGA rework station ?
– Precision and Control: BGA rework station offers unparalleled precision in handling small, densely packed components, ensuring reliable solder joints and minimizing the risk of damage.
– Versatility: These stations can handle a wide range of BGA components, regardless of size, pitch, or material, making them versatile tools in diverse electronics repair and manufacturing environments.
– Time Efficiency: Compared to manual rework methods, BGA rework station significantly reduces turnaround times for repairs and modifications, improving overall productivity.
How does the BGA rework station work?
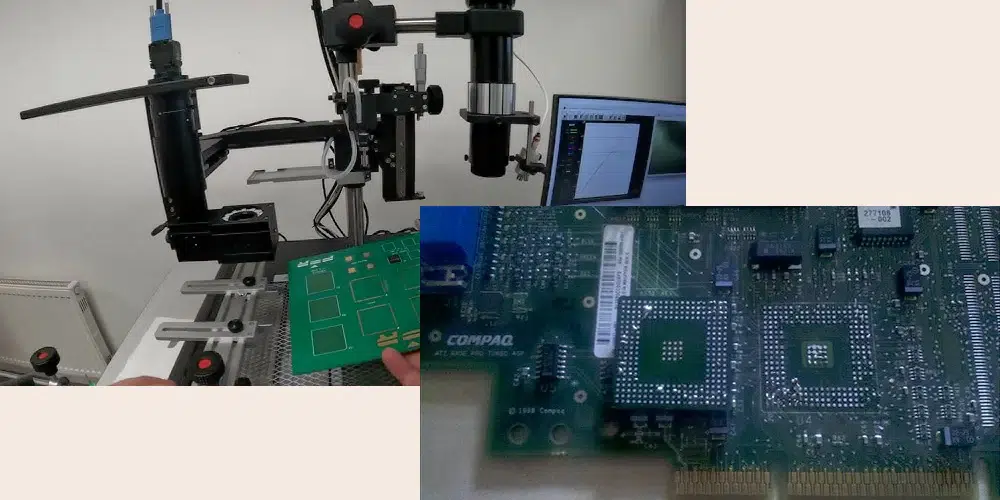
Process of BGA Reworking:
Component Removal: The first step in BGA reworking is to remove the faulty or old BGA component from the PCB. This is typically done using specialized equipment such as a BGA rework station. The station heats the solder joints underneath the BGA with precision-controlled temperature and airflow, melting the solder and allowing the component to be lifted off the board.
Cleaning: After removal, any remaining solder and flux residue on the PCB pads and surrounding areas are cleaned thoroughly. This ensures a clean surface for soldering the new component and prevents contamination that could affect solder joint integrity.
Inspection: The PCB is then inspected under magnification to assess the condition of the pads and ensure no damage occurred during the removal process. Any damaged pads or traces may need to be repaired before proceeding.
Component Replacement: Once the PCB is prepared, a new BGA component is placed onto the board. Precision is crucial during this step to align the solder balls of the BGA with the corresponding pads on the PCB. Advanced BGA rework stations often include optical alignment systems to assist in achieving accurate placement.
Soldering: The final step involves soldering the new BGA component to the PCB. Again, a BGA rework station is used to apply controlled heat and solder paste or solder balls to create reliable electrical connections between the BGA and the PCB pads. Proper soldering ensures mechanical stability and electrical continuity required for the component to function correctly.
Testing: After soldering, the reworked PCB undergoes testing to verify the functionality of the replaced BGA component and ensure that all connections are intact. Functional testing may involve powering up the board and running diagnostic tests to confirm proper operation.
What temperature should a BGA rework station be set at?
Setting the temperature on a BGA rework station is a critical aspect of the rework process to ensure proper soldering without damaging the components or the PCB. The exact temperature settings can vary depending on several factors such as the type of BGA component, the size and pitch of the solder balls, the type of solder used, and the specific requirements of the PCB assembly. Here are some general guidelines:
1. Preheating Temperature: Before directly heating the BGA component, it’s often beneficial to preheat the entire PCB to reduce thermal shock and stress. Preheating temperatures typically range from 100°C to 150°C (212°F to 302°F), depending on the board’s size and thermal mass.
2. Soldering Temperature: The temperature at which the solder balls under the BGA component are reflowed usually ranges between 200°C to 260°C (392°F to 500°F). This temperature range ensures that the solder melts adequately for the BGA component to be lifted off or placed onto the PCB.
3. Profile Settings: Many BGA rework stations allow you to create temperature profiles that include ramp-up, soak, and ramp-down phases. These profiles help manage the heating process more effectively, minimizing thermal stress and ensuring consistent soldering results.
4. Component-Specific Considerations: Some BGA components and PCB assemblies may have specific temperature requirements specified by the manufacturer. It’s essential to consult the component datasheet or assembly guidelines for recommended reflow temperatures.
In summary, while the exact temperature setting for a BGA rework station can vary, a typical range for soldering temperatures is between 200°C to 260°C (392°F to 500°F). Preheating the PCB beforehand and using temperature profiles can further optimize the rework process, ensuring successful component removal, replacement, or repair while preserving the integrity of the PCB and components.
Future Trends
As electronic devices continue to evolve with smaller and more complex designs, the demand for advanced BGA rework station is expected to grow. Future innovations may focus on integrating artificial intelligence for automated rework processes and enhancing compatibility with emerging materials and component technologies.
In conclusion, BGA rework station is indispensable tool in the electronics industry, enabling precise and efficient repair, refurbishment, and prototype development of BGA components. The ability of BGA rework stations to handle intricate soldering processes with control and reliability underscores their importance in maintaining and advancing electronic device technology.
A BGA rework station is a sophisticated piece of equipment designed specifically to remove, replace, and rework BGA components on printed circuit boards (PCBs). It incorporates precise control over temperature, airflow, and alignment, crucial for handling the delicate soldering processes associated with BGAs.
Heating System
Optical Alignment Systems
Temperature Control
Vacuum Handling Tools
Software Control
Repair and Refurbishment
Prototype Development
Component Upgrades