Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) are the backbone of modern electronics, providing both the physical and electrical connections needed for electronic components to function. While the full assembly of a PCB with components is often the focus, an empty PCB board—often referred to as a “bare PCB”—is a crucial component in the electronics manufacturing process. This article delves into the intricacies of empty PCB board, including their design, manufacturing process, and applications.
What is an Empty PCB Board?
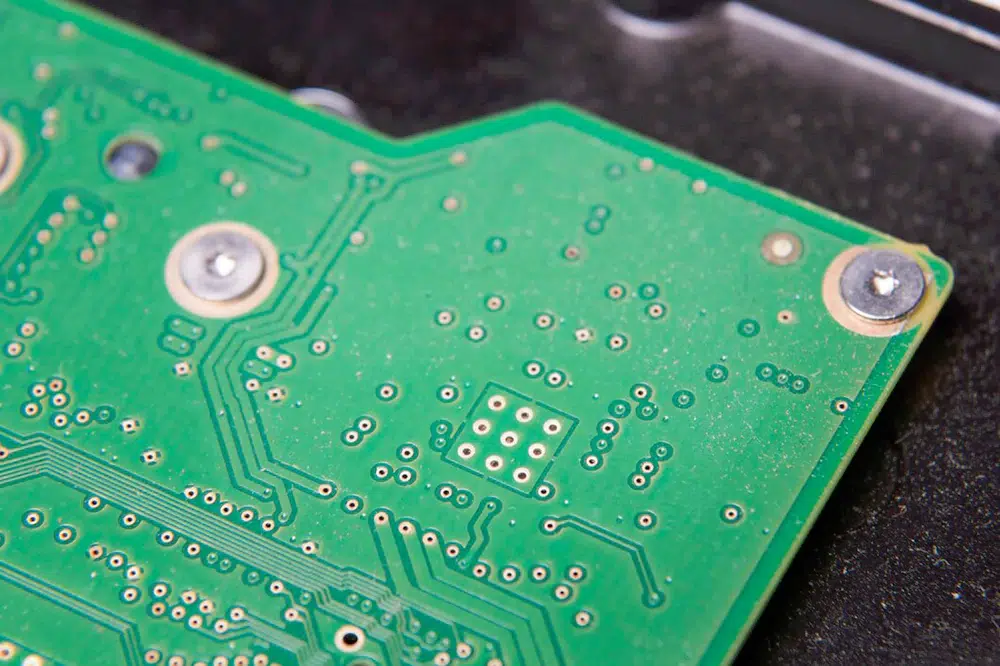
An empty PCB board is a circuit board that has been fabricated but does not yet have any electronic components soldered onto it. It consists of a flat, insulating substrate, typically made of materials like fiberglass or plastic, with conductive pathways printed on its surface. These pathways, usually made of copper, form the circuit traces that will eventually connect various electronic components once they are installed.
How to design empty PCB board?
1. Material Selection:
– Substrate: The most common substrate material is FR-4, a composite of woven glass fabric and epoxy resin. For specialized applications, other materials like polyimide or ceramics might be used.
– Copper Thickness: The thickness of the copper layer is crucial for determining the current-carrying capacity and heat dissipation characteristics of the PCB.
2. Layer Count:
– Single-Sided: One layer of copper, used for simpler, low-density applications.
– Double-Sided: Copper layers on both sides of the board, connected through vias (holes).
– Multilayer: More than two layers of copper, separated by insulating layers, used for complex, high-density designs.
3. Trace Design:
– Trace Width: The width of the copper traces must be carefully designed to handle the electrical current without excessive heating.
– Spacing: Adequate spacing between traces is essential to prevent short circuits and signal interference.
4. Hole Sizes and Placement:
– Via Holes: Used for connecting traces between different layers.
– Mounting Holes: For securing the PCB to enclosures or other hardware.
How to manufacture empty PCB board?
1. Design Phase:
– Schematic Capture: The electronic circuit is designed using CAD software, creating a schematic that defines the connections between components.
– PCB Layout: The schematic is translated into a PCB layout, where the physical placement of traces, holes, and other features is defined.
2. Fabrication:
– Printing: A photographic or laser etching process is used to transfer the PCB design onto a copper-clad substrate.
– Etching: Unwanted copper is removed using chemical etching, leaving behind the desired circuit traces.
– Drilling: Holes for vias and component leads are drilled.
– Plating: Vias are plated with copper to ensure electrical connectivity between layers.
– Inspection: The bare PCB is inspected for manufacturing defects and to ensure that it meets design specifications.
3. Testing:
– Electrical Testing: Verifying that the connections are correct and there are no shorts or opens in the circuitry.
What the applications of empty PCB board?
1. Prototyping:
– Rapid Prototyping: Engineers and designers use empty PCBs to create and test prototypes of new electronic devices before committing to full-scale production.
2. Educational Purposes:
– Learning Tool: Empty PCBs are used in educational settings to teach students about electronics, circuit design, and PCB assembly.
3. DIY Projects:
– Hobbyist Use: Electronics enthusiasts and hobbyists use empty PCBs to build custom circuits and devices tailored to their specific needs.
4. Industrial Applications:
– Customization: In industries requiring custom electronics, empty PCBs are fabricated to specific designs to suit particular applications.
List some empty PCB board manufacturers in the world
There are numerous companies worldwide specializing in the manufacturing of empty PCB (Printed Circuit Board) boards. These manufacturers offer a range of services, including prototyping, small-batch production, and large-scale manufacturing. Here is a list of some prominent PCB board manufacturers globally:
1. PCBWay
– Headquarters: Shenzhen, China
– Website: [pcbway.com](https://www.pcbway.com)
– Specialty: Offers PCB prototyping, manufacturing, and assembly services.
2. JLCPCB
– Headquarters: Shenzhen, China
– Website: [jlcpcb.com](https://www.jlcpcb.com)
– Specialty: Known for cost-effective PCB prototyping and small-batch production.
3. Advanced Circuits (4PCB)
– Headquarters: Aurora, Colorado, USA
– Website: [4pcb.com](https://www.4pcb.com)
– Specialty: Provides PCB prototyping, manufacturing, and assembly services.
4. Eurocircuits
– Headquarters: Mechelen, Belgium
– Website: [eurocircuits.com](https://www.eurocircuits.com)
– Specialty: Specializes in PCB prototyping and small to medium-scale production.
5. Nippon Mektron
– Headquarters: Tokyo, Japan
– Website: [mektron.co.jp](https://www.mektron.co.jp)
– Specialty: A leading manufacturer of flexible PCBs and other advanced PCB technologies.
6. Sanmina Corporation
– Headquarters: San Jose, California, USA
– Website: [sanmina.com](https://www.sanmina.com)
– Specialty: Provides a range of PCB manufacturing and assembly services, including high-density interconnect (HDI) boards.
7. Zhen Ding Technology Holding Limited
– Headquarters: Taipei, Taiwan
– Website: [zdtc.com.tw](http://www.zdtc.com.tw)
– Specialty: Offers a wide variety of PCBs, including high-frequency and flexible circuits.
8. Unimicron Technology Corporation
– Headquarters: Taoyuan, Taiwan
– Website: [unimicron.com](http://www.unimicron.com)
– Specialty: Known for its production of high-density PCBs and advanced interconnect technologies.

Conclusion
Empty PCB boards are more than just a starting point in the electronics manufacturing process; they are a fundamental element that bridges the gap between theoretical design and practical implementation. Understanding the design, manufacturing, and application aspects of empty PCBs is essential for anyone involved in electronics, from hobbyists to professionals. By mastering these elements, one can ensure the creation of functional, reliable, and efficient electronic devices that drive innovation in technology.
An empty PCB board is a circuit board that has been fabricated but does not yet have any electronic components soldered onto it.
PCB Design
PCB Fabrication
PCB Testing
Prototyping
Educational Purposes
DIY Projects
Industrial Applications