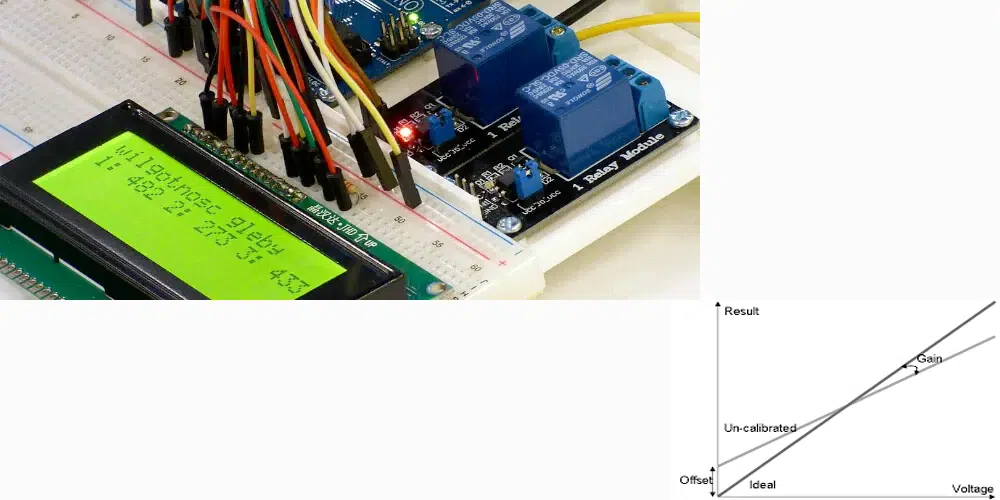
Printed Circuit Board Assembly (PCBA) function testing is a crucial step in the manufacturing process of electronic devices. It ensures that each component on the PCB operates correctly and meets the desired specifications. Gain and offset are two essential parameters in PCBA function testing, playing significant roles in determining the accuracy and reliability of the test results.
What is Gain and Offset?
Before delving into their relevance in PCBA function testing, let’s define gain and offset:
Gain: In electronics, gain refers to the ratio of the output signal magnitude to the input signal magnitude. It signifies the amplification or attenuation of a signal by a circuit or device. Gain is typically expressed in decibels (dB) or as a unitless ratio.
Offset: Offset, on the other hand, represents a constant value added to or subtracted from a signal. It accounts for any inherent bias or error in the measurement system and ensures accurate calibration and alignment.
Importance of Gain and Offset in PCBA Function Testing
In PCBA function testing, gain and offset calibration are essential for several reasons:
1. Accuracy: Correct gain and offset settings ensure that test measurements accurately reflect the true performance of the device under test (DUT). Any inaccuracies in gain or offset can lead to erroneous test results, potentially causing defective products to go undetected or functional units to be erroneously rejected.
2. Consistency: Consistent gain and offset settings across different test stations and manufacturing runs are critical for maintaining uniformity in test results. This consistency allows for reliable comparison of test data and facilitates troubleshooting and root cause analysis in case of failures or discrepancies.
3. Optimization: Properly calibrated gain and offset parameters optimize the sensitivity and dynamic range of the test system, enabling it to detect subtle deviations or abnormalities in the DUT’s behavior. This optimization enhances the test system’s capability to identify defects or performance variations within acceptable tolerance limits.
4. Performance Characterization: Gain and offset adjustments are often part of the process of characterizing the performance of test instruments and equipment. By calibrating these parameters, manufacturers can ensure that their test systems meet specified performance criteria and comply with industry standards.
Implementation of Gain and Offset Calibration in PCBA Function Testing
Achieving accurate gain and offset calibration in PCBA function testing involves several steps and techniques:
1. Calibration Standards: Utilize precision calibration standards, such as resistors, capacitors, or reference voltage sources, with known values to calibrate gain and offset settings. These standards serve as benchmarks for establishing the desired response of the test system.
2. Instrumentation Calibration: Calibrate the test instruments, including multimeters, oscilloscopes, signal generators, and data acquisition systems, to ensure accurate measurement and signal processing. This calibration involves adjusting gain and offset parameters to match the expected values of the calibration standards.
3. Software Calibration: Implement software-based calibration algorithms or procedures to automate the adjustment of gain and offset settings in the test software or firmware. This approach streamlines the calibration process and minimizes human error while ensuring consistency and repeatability.
4. Test Fixture Calibration: Calibrate the test fixtures and probes used for contacting the DUT to account for any impedance mismatches, signal attenuation, or interference. Proper fixture calibration helps maintain signal integrity and minimizes measurement errors attributable to the test setup.
5. Dynamic Compensation: Employ dynamic compensation techniques, such as auto-ranging, auto-zeroing, or adaptive filtering, to continuously adjust gain and offset parameters in real-time based on the characteristics of the test signals and environmental conditions. Dynamic compensation enhances the robustness and accuracy of the test system, particularly in dynamic or noisy testing environments.
6. Verification and Validation: Validate the accuracy and effectiveness of gain and offset calibration by performing verification tests using known test patterns or simulated DUTs. This validation process ensures that the calibration procedures yield the desired results and meet the specified performance requirements.
Conclusion
Gain and offset calibration are critical aspects of PCBA function testing, essential for achieving accurate, consistent, and reliable test results. By understanding their significance and implementing proper calibration techniques, manufacturers can enhance the quality, efficiency, and competitiveness of their products while ensuring compliance with industry standards and customer expectations. Effective gain and offset calibration empower manufacturers to deliver electronic devices with superior performance, functionality, and durability, driving innovation and advancement in the electronics industry.