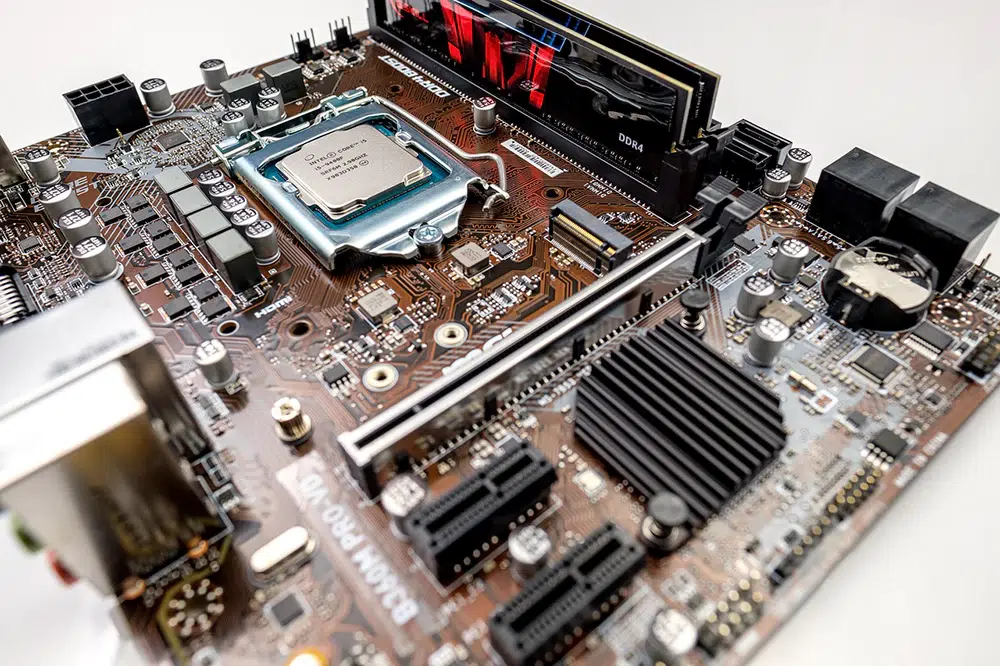
In the realm of electronics, the motherboard is the central hub that orchestrates the functioning of a computer system. At its core, it’s built on a specialized type of printed circuit board (PCB) designed to connect and manage various components. This article delves into the intricacies of motherboard PCB, its design, manufacturing, and role in modern technology.
What is a Motherboard PCB?
A motherboard PCB is a complex, multi-layered circuit board that serves as the main platform for mounting and interconnecting various electronic components of a computer. It provides the necessary pathways for electrical signals and power to flow between the central processing unit (CPU), memory, storage devices, and peripheral components.
What components are concluded in motherboard PCB?
1. CPU Socket: The CPU socket is a critical part of the motherboard where the processor is installed. It ensures proper electrical contact and cooling.
2. RAM Slots: These slots accommodate the system memory (RAM). They are typically designed to handle high-speed data transfer and support dual-channel or multi-channel configurations for enhanced performance.
3. Expansion Slots: These slots, such as PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express) and PCI (Peripheral Component Interconnect), allow additional cards to be installed, such as graphics cards, sound cards, and network cards.
4. Chipset: The chipset manages communication between the CPU, memory, and peripheral devices. It often includes northbridge and southbridge components, although modern designs integrate many of these functions into a single chip.
5. Power Connectors: These connectors supply power to the motherboard and its components. They include the main 24-pin ATX connector and additional connectors for CPU and graphics cards.
6. Storage Connectors: Interfaces like SATA (Serial ATA) and M.2 slots are used for connecting storage devices such as hard drives, SSDs (solid-state drives), and optical drives.
7. I/O Ports: The rear panel of the motherboard features various ports for external connections, including USB ports, audio jacks, Ethernet ports, and video outputs like HDMI and DisplayPort.
8. BIOS/UEFI Chip: This chip contains the firmware that initializes hardware during the boot process and provides a setup interface for system configuration.
What should be considered when design a motherboard PCB?
Designing a motherboard PCB involves several critical considerations:
1. Layer Count: Motherboards are typically multi-layered PCBs, with higher-end models featuring up to 12 or more layers. These layers include signal layers, power planes, and ground planes, all crucial for managing signal integrity and power distribution.
2. Signal Integrity: High-speed signal paths, such as those for PCIe or memory, require careful routing to minimize interference and signal degradation. Designers use techniques like differential signaling and impedance matching to maintain signal quality.
3. Thermal Management: Motherboards must manage heat generated by high-performance components. Design elements such as heat sinks, thermal pads, and optimized airflow paths help dissipate heat and prevent overheating.
4. Power Distribution: Efficient power distribution is vital for stable operation. The PCB must be designed to handle varying power requirements and minimize voltage drops across different components.
5. Component Placement: Strategic placement of components is essential to reduce signal interference, optimize performance, and ensure compatibility with other hardware. This involves careful planning of the PCB layout to accommodate all necessary parts while maintaining a compact form factor.
6. Manufacturing Constraints: Design must account for manufacturing limitations, such as the minimum trace width and spacing, to ensure the PCB can be produced reliably and cost-effectively.
How to manufacture a motherboard PCB?
The manufacturing of motherboard PCBs involves several steps:
1. Design and Prototyping: The design process begins with creating a schematic diagram and PCB layout using specialized software. Prototypes are then produced to test and validate the design.
2. Fabrication: The PCB is fabricated through processes like etching and layering. A raw PCB starts with a laminate base material, typically FR4 (a fiberglass-epoxy composite), which is then coated with a layer of copper. The copper is patterned to create the circuit traces and pads.
3. Assembly: After fabrication, components are mounted on the PCB using surface-mount technology (SMT) or through-hole technology. SMT components are placed on the board and soldered using automated machines, while through-hole components are inserted and soldered manually or with automated machines.
4. Testing and Quality Control: Rigorous testing ensures the motherboard meets quality standards. This includes electrical tests, thermal tests, and functional tests to verify that all components work as intended.
5. Packaging and Distribution: Once tested, the motherboards are packaged and prepared for distribution to manufacturers, retailers, or directly to consumers.
PCB motherboard manufacturers- produce PCB for your motherboard
PCBWay
Website:https://www.pcbway.com/
JLCPCB
Website:https://jlcpcb.com/
Advanced Circuits
Website:https://www.advancedpcb.com/en-us/
TTM Technologies
Website:https://www.ttm.com/en
Zhen Ding Technology
Website:https://www.zdtco.com/en/about/group
IBE Electronics
Website:https://www.pcbaaa.com/
Conclusion
Motherboard PCBs are integral to the functionality of modern electronic systems, acting as the central nervous system that connects and manages various components. Understanding their design, manufacturing, and evolution provides insight into how technology continues to advance and shape our digital world.
IBE is a leading OEM/ODM/EMS manufacturer specializing in customized PCB manufacturing and assembly, especially motherboard PCB. Our expertise spans designing intricate circuit board layouts tailored to your specifications and assembling them with precision. From initial concept to final product, we offer end-to-end solutions, ensuring high-quality and reliable PCBs. Our advanced manufacturing capabilities and state-of-the-art equipment enable us to handle diverse projects, delivering efficient and cost-effective solutions. Whether you need prototypes or large-scale production, our dedicated team is committed to meeting your unique requirements and exceeding industry standards. Partner with us for innovative, customized PCB solutions that drive your success.
A motherboard PCB is the primary circuit board in a computer that connects and allows communication between various components, such as the CPU, RAM, and storage devices.
Common components include the CPU socket, RAM slots, chipset, PCIe slots, SATA connectors, power connectors, and various headers for additional peripherals.
A motherboard PCB is specifically designed for computing and typically includes more complex and numerous connections and traces compared to other PCBs, which might be simpler and serve different functions in various devices.