In the electronics industry, PCB (Printed Circuit Board) is an indispensable and important component, and PCB packaging is one of the crucial aspects. So, what exactly is PCB packaging, and what are the common types of PCB packaging?
Basic Concepts of PCB Packaging
PCB packaging refers to the process of protecting and enclosing printed circuit boards (PCBs) within a protective housing or casing. This packaging is essential to safeguard the delicate electronic components and circuits on the PCB from environmental factors, mechanical damage, and electromagnetic interference (EMI).
The main purpose of PCB packaging is to protect the internal electronic components from the external environment, such as dust, moisture and mechanical shock. At the same time, good packaging can also improve the heat dissipation performance of the circuit board to ensure that the components will not be damaged by overheating after a long period of time.
Common PCB Package Types
DIP Package (Dual In-line Package)
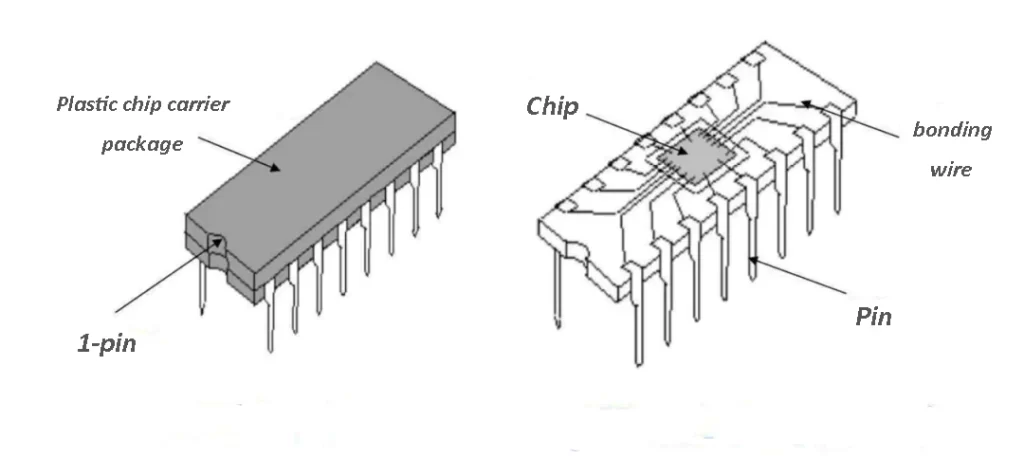
DIP package, also known as Dual In-line Package, is one of the earliest packaging forms. Its characteristic is that there are two parallel rows of pins on a rectangular plastic or ceramic base, which can be inserted.
DIP packaging has the advantages of low cost and easy operation, so it is still widely used in some traditional electronic devices.
SOP Package (Small Outline Package)
SOP package, also known as Small Outline Package, is a type of surface mount package. The outline of SOP package is more compact than DIP package, suitable for high-density installation.
The pins of SOP package are led out from both sides of the package, forming a gull-wing shape. This design enables SOP package to have better self-alignment capability during soldering, thus improving production efficiency.
QFP Package (Quad Flat Package)
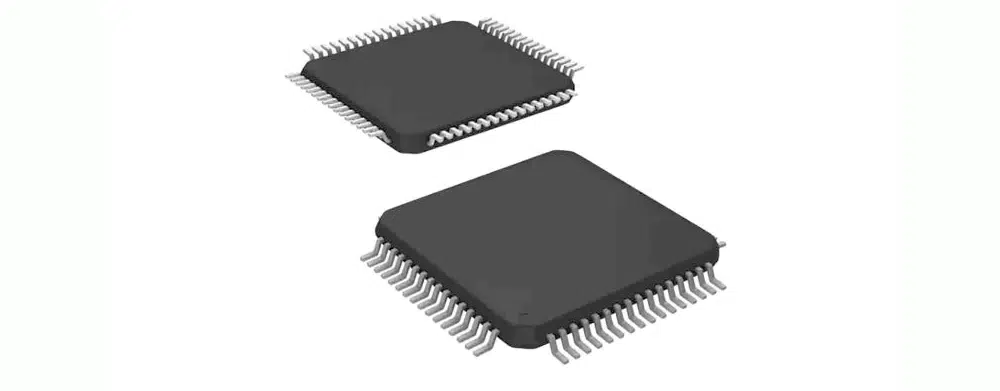
QFP package, also known as Quad Flat Package, is a type of surface mount package with multiple pins. Its pins are led out from four sides, forming a flat shape.
QFP package has the advantages of a large number of pins and high assembly density, thus it has been widely used in high-performance electronic devices.
BGA Package (Ball Grid Array Package)
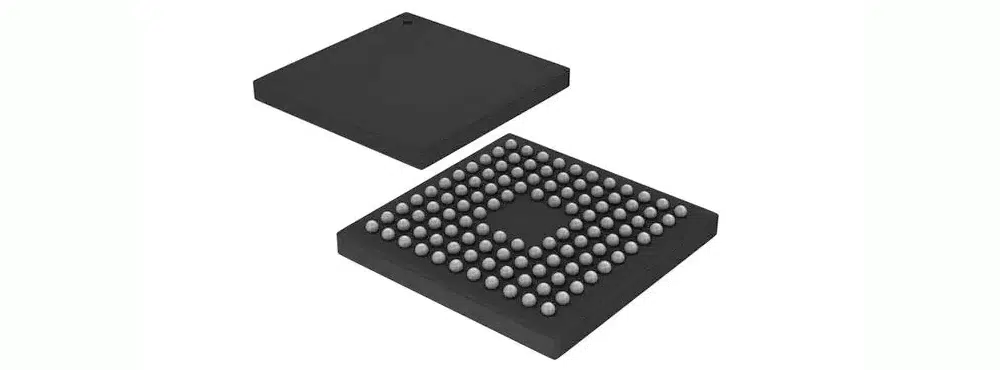
BGA package, also known as Ball Grid Array Package, is an advanced packaging technology. Its characteristic is that there are many tiny solder balls as pins on the bottom of the package, arranged in a grid pattern.
BGA package has the advantages of a high number of pins, high density, and high performance, making it especially suitable for situations requiring a large number of pins and high-speed data transmission.
CSP Package (Chip Scale Package)
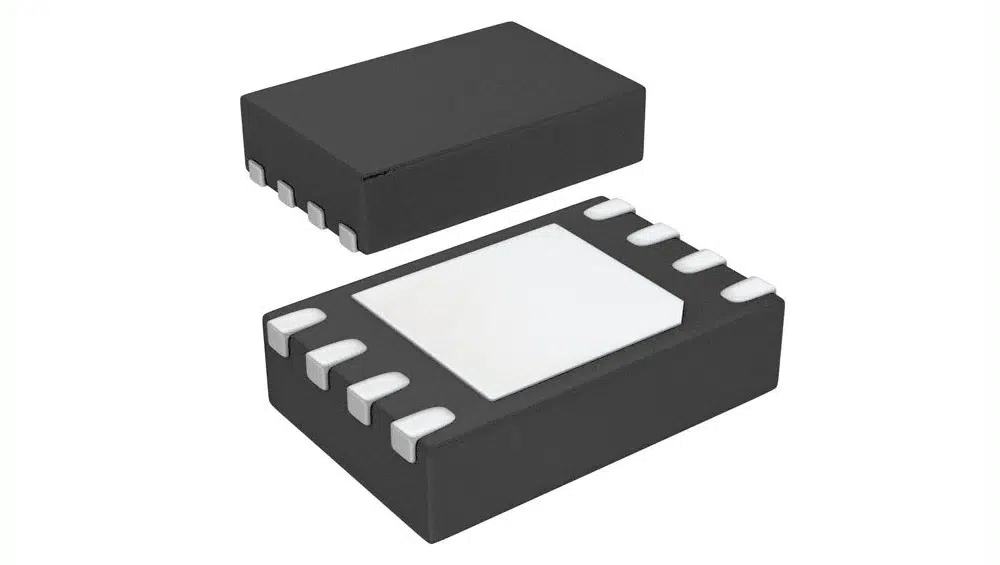
CSP package, also known as Chip Scale Package, is a packaging form with a size close to that of the chip itself.
CSP package has extremely small volume and weight, making it very suitable for portable electronic devices. Due to its high integration and low cost, CSP packaging has experienced rapid development in recent years.
QFN Package (Quad Flat No-lead Package)
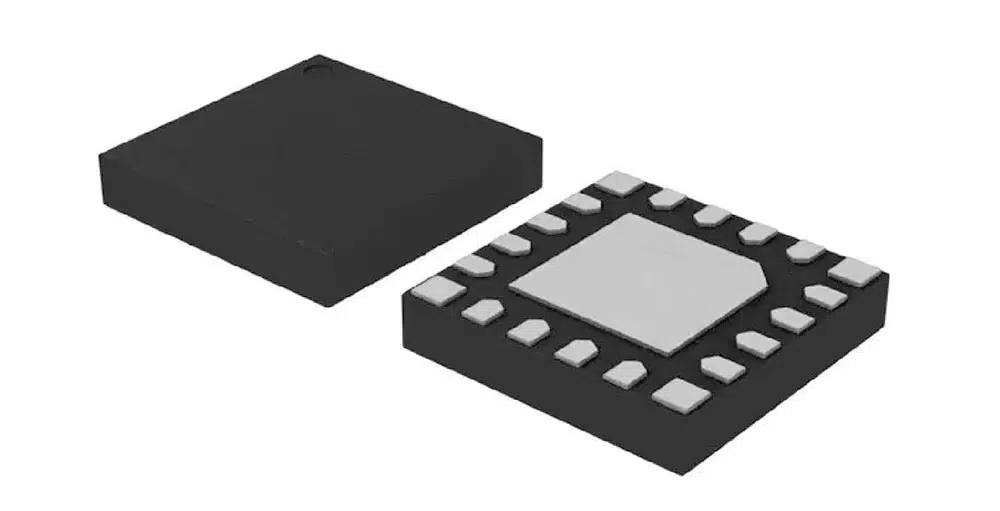
QFN package, also known as Quad Flat No-lead Package, is a type of surface mount package without pins. The characteristic of QFN package is to use a large exposed pad in the center of the package bottom for heat dissipation, while there are electrode contact points around the package, eliminating the need for additional pins.
This packaging method not only saves space but also improves heat dissipation performance, thus it has been widely used in applications with high requirements for space and heat dissipation.
Factors to Consider When Choosing PCB Packaging
When selecting PCB packaging, several factors need to be considered to ensure the stability and reliability of the circuit. Here are some key considerations:
Electrical Performance: Different packaging forms have varying effects on electrical performance. For example, BGA packaging, due to its pin distribution on the bottom of the package, offers better electrical performance and higher data transfer rates.
Heat Dissipation: Heat dissipation performance of the packaging form is also an important consideration. For instance, QFN packaging utilizes a large exposed pad on the bottom for heat dissipation, thus providing good heat dissipation performance.
Space Constraints: In applications with space limitations, it’s necessary to choose smaller packaging forms, such as CSP packaging.
Cost Consideration: The cost of packaging forms is also a factor to consider. Generally, advanced packaging technologies like BGA and CSP tend to have relatively higher costs.
Maintainability: For devices requiring frequent maintenance or component replacement, it’s advisable to choose packaging forms that are easy to disassemble and install, such as DIP packaging.











