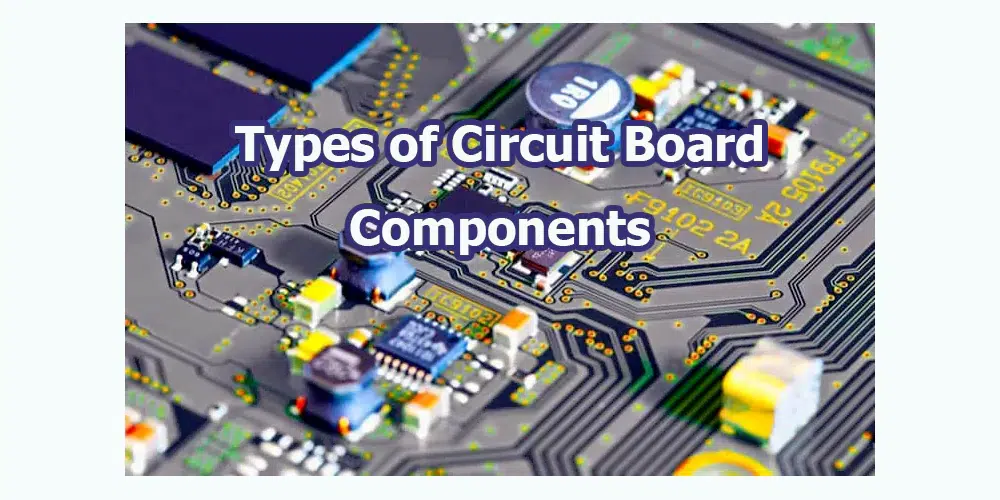
Circuit boards play a crucial role in the functioning of electronic devices, serving as the foundation for connecting various electrical components. These boards consist of multiple circuit board components that work together to facilitate the desired electrical behavior. Understanding the different types and functions of circuit board components is essential for designing and building reliable electronic devices.
Types of Circuit Board Components
Circuit board components can be broadly categorized into two main types: active and passive components.
Active Circuit Board Components
Active components are those that require an external power source to operate. These components control the flow of electrical signals and are responsible for amplification, oscillation, and switching within the circuit. Integrated circuits (ICs), transistors, and diodes are common examples of active circuit board components.
Integrated circuits, also known as ICs or microchips, are miniaturized electronic circuits that are etched onto a small semiconductor material. They can contain thousands or even millions of individual components, such as transistors, resistors, and capacitors, all integrated onto a single chip. ICs are widely used in various electronic devices, including computers, smartphones, and consumer electronics.
Transistors are fundamental active components that regulate the flow of electrical signals in a circuit. They can amplify weak signals, switch them on or off, or act as voltage regulators. Different types of transistors, such as bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) and field-effect transistors (FETs), offer specific advantages and are suitable for various applications.
Diodes are electronic components that allow current to flow in one direction while blocking it in the opposite direction. They are commonly used in rectification circuits, voltage regulation, and signal demodulation. Diodes come in various types, including Schottky diodes, Zener diodes, and light-emitting diodes (LEDs).
Passive Circuit Board Components
Passive components, unlike active components, do not require an external power source to function. They modify the electrical properties of a circuit without amplifying or switching signals. The most common passive components found on circuit boards are resistors, capacitors, and inductors.
Resistors are components that resist the flow of electrical current. They are used to control current levels, divide voltage, and provide stability in circuits. Different types of resistors, such as carbon film resistors, metal film resistors, and variable resistors, offer specific resistance values and power ratings.
Capacitors store and release electrical energy in the form of electric fields. They are used for energy storage, filtering, timing, and decoupling in electronic circuits. Capacitors can be categorized based on their dielectric material and construction, such as ceramic capacitors, electrolytic capacitors, and film capacitors.
Inductors are passive components that store energy in the form of magnetic fields. They resist changes in current flow and are used for filtering, energy storage, and signal processing. Inductors can be found in various forms, including air-core inductors, ferrite-core inductors, and toroidal inductors.
Additional Circuit Board Components
Apart from active and passive components, circuit boards also incorporate other components for enhanced functionality and connectivity. Some of these components include connectors, switches, and LEDs.
Connectors are essential for establishing electrical and mechanical connections between different parts of a circuit. They come in various types, such as pin headers, sockets, and terminal blocks, and enable the easy attachment and detachment of wires, cables, and other devices.
Switches are electrical components used to control the flow of current in a circuit. They can be mechanical or electronic and are commonly used for on/off operations, mode selection, and circuit routing. Switches are available in different configurations, including push-button switches, toggle switches, and rotary switches.
LEDs (Light Emitting Diodes) are semiconductor devices that emit light when an electric current passes through them. They are widely used for indication, lighting, and display purposes in electronic devices. LEDs offer advantages such as low power consumption, long lifespan, and color variety.
Importance of Circuit Board Component Selection
The chosen components should meet the specific requirements of the circuit, ensuring optimal functionality and compatibility. Proper component selection also contributes to the efficiency, stability, and safety of the circuit, minimizing the risk of failures or malfunctions.
Circuit Board Assembly and Testing
Once the components are selected, the circuit board assembly process begins. This involves placing the components onto the circuit board and soldering them into position. Advanced manufacturing techniques, including surface mount technology (SMT) and through-hole technology (THT), are used for efficient and precise component placement.
After assembly, the circuit board undergoes rigorous testing to ensure proper functionality and adherence to design specifications. Testing methods such as automated optical inspection (AOI), in-circuit testing (ICT), and functional testing are employed to detect any defects or faults in the circuit.
Quality control measures are implemented throughout the assembly and testing processes to maintain high standards and minimize production issues. These measures include strict adherence to industry standards, comprehensive inspection procedures, and continuous process improvement initiatives.
Future trends and advancements in circuit board components are shaping the landscape of electronics. As technology progresses, circuit board components are evolving to meet the demands of smaller, faster, and more efficient devices. Some notable trends include:
Miniaturization: The ongoing trend of miniaturization allows for smaller and more compact electronic devices. Circuit board components are being developed with reduced sizes and increased functionality to accommodate the shrinking form factors of modern devices.
Integration: Integrated circuit technology continues to advance, enabling more complex functionality in a single chip. System-on-Chip (SoC) designs integrate multiple functions, such as processing, memory, and communication, onto a single chip, optimizing performance and reducing space requirements.
Enhanced Performance: Circuit board components are being designed to offer improved performance characteristics. This includes higher processing speeds, increased memory capacities, lower power consumption, and improved signal integrity. These advancements contribute to the overall performance and efficiency of electronic devices.
Connectivity: With the rise of the Internet of Things (IoT) and smart devices, circuit board components are being developed with enhanced connectivity features. Components with built-in wireless capabilities, such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and cellular connectivity, enable seamless communication and integration with other devices and networks.
Advanced Materials: New materials and manufacturing techniques are being explored to improve the performance and reliability of circuit board components. For example, the use of flexible substrates and printed electronics allows for the development of flexible and bendable circuits, opening up new possibilities for wearable technology and flexible displays.
Energy Efficiency: Energy efficiency is a key focus in circuit board component development. Components with lower power consumption contribute to longer battery life in portable devices and reduced energy consumption in larger systems. This not only benefits the environment but also enhances the user experience.
High-Speed Communication: As data transmission speeds continue to increase, circuit board components are being designed to support high-speed communication protocols, such as USB 3.1, Thunderbolt, and PCIe. These advancements facilitate faster data transfer rates, enabling seamless multimedia streaming, gaming, and data-intensive applications.

Conclusion
Circuit board components are the building blocks of electronic devices, playing a critical role in their functionality and performance. Understanding the different types of components, their functions, and how they interact is essential for designing and constructing reliable circuits.
The selection of circuit board components should be based on factors such as the specific application requirements, electrical characteristics, and environmental considerations. Proper assembly and testing processes ensure the quality and reliability of the final product.
Looking ahead, future advancements in circuit board components will continue to drive innovation in the electronics industry. Miniaturization, integration, enhanced performance, connectivity, advanced materials, energy efficiency, and high-speed communication are key areas where significant progress is being made.
As technology evolves, circuit board components will continue to evolve, enabling the development of smaller, more powerful, and more connected electronic devices that enhance our daily lives.
The essential circuit board components include active components like integrated circuits, transistors, and diodes, as well as passive components like resistors, capacitors, and inductors.
Active components require an external power source to operate and control electrical signals, while passive components modify electrical properties without amplification or switching.
Important factors include component specifications, electrical characteristics, thermal considerations, and environmental conditions.