PCB (Printed Circuit Board) is an indispensable part of electronic products and is widely used in various electronic devices, such as computers, mobile phones, televisions, etc. The importance of PCBs in electronics is self-evident, so there are many different types during the manufacturing process. Among them, the most common are single-layer boards and multi-layer boards. So, what is the difference between single Layer PCBs and multilayer PCBs ? How do we choose?
Overview of single Layer PCBs and multilayer PCBs
Single Layer PCBs
Single Layer Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) are the simplest and most basic type of PCBs, where the electrical components are mounted on a single side of a board made of a conductive material, typically copper. These PCBs are generally used for low-complexity and low-density applications such as power supplies, sensors, and simple control circuits.
Multilayer PCBs
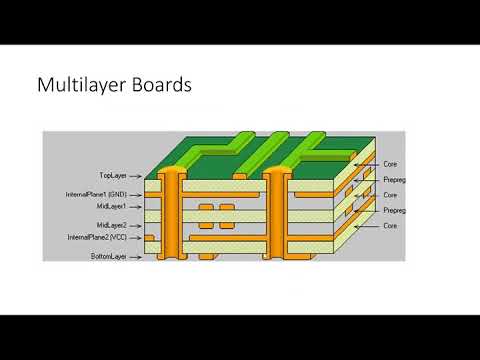
Multilayer PCBs, on the other hand, have multiple layers of conductive material sandwiched between insulating layers, allowing for a higher density of components and more complex circuits. These PCBs are used in high-density applications such as computers, smartphones, and other electronics with complex circuits.
Advantages and disadvantages of single layer PCBs and multilayer PCBs
Single Layer PCBs
Single Layer PCBs have several advantages such as low cost, ease of repair, and easier design process, making them suitable for low-volume and low-cost products. However, they also have several disadvantages such as limited space for components and routing, difficulty in controlling emissions and susceptibility to interference, and limited thermal management capabilities.
Multilayer PCBs
Multilayer PCBs have many advantages including high density, improved thermal management, and reduced electromagnetic interference (EMI). However, they also have several disadvantages such as high cost, complex manufacturing process, and difficult repair process. Additionally, the design process for multilayer PCBs is more complex, requiring specialized tools and expertise.
Factors to consider when selecting single layer or multilayer PCBs
When deciding between single layer and multilayer PCBs, it is important to consider several factors such as the complexity of the circuit, the density of components, the size and weight of the product, and the cost constraints. Additionally, the intended use of the product, the operating environment, and the thermal management requirements should also be taken into account.
Design tips for single layer PCBs and multilayer PCBs
Design tips for single layer PCBs
When designing single layer PCBs, it is important to keep the design simple and minimize the number of components. Additionally, careful consideration should be given to the routing of signals and the placement of components to minimize interference and improve performance. Proper thermal management techniques, such as the use of vias and heat sinks, should also be implemented to manage heat dissipation.
Design tips for multilayer PCBs
When designing multilayer PCBs, it is important to consider the placement of components, the routing of signals, and the stackup of the layers. Additionally, special care should be taken to manage EMI and to control the flow of heat. Proper testing and verification should also be performed to ensure the quality of the final product.
Manufacturing considerations of single layer PCBs and multilayer PCBs
Both single layer and multilayer PCBs have unique manufacturing challenges, and it is important to choose a manufacturer with experience and expertise in the specific type of PCB being produced. For example, multilayer PCBs require specialized equipment and processes, and it is important to work with a manufacturer that has experience with these processes. Additionally, proper testing and verification should be performed to ensure the quality of the final product.
Cost comparison
Single layer PCBs are generally less expensive than multilayer PCBs due to the simpler manufacturing process and lower complexity of the design. However, the cost difference will depend on several factors, such as the size of the board, the density of components, and the complexity of the circuit. It is important to consider the overall cost of the project, including both the cost of the PCB and the cost of any associated components, when deciding between single layer and multilayer PCBs.
Additionally, the cost of manufacturing and the cost of repairs should also be taken into account. In some cases, the higher initial cost of a multilayer PCB may be offset by the improved performance, reduced maintenance, and longer lifespan of the product.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the choice between single layer and multilayer PCBs depends on the specific requirements of the project. Single layer PCBs are suitable for low-complexity, low-density applications, while multilayer PCBs are suitable for high-density, complex applications.
The factors to be considered when choosing between single layer and multilayer PCBs include the complexity of the circuit, the density of components, the cost, and the intended use of the product. Design considerations, manufacturing considerations, and cost comparisons should all be taken into account to make an informed decision. Ultimately, the right choice will depend on the specific requirements of the project and the goals of the designer.
Single Layer Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) are the simplest and most basic type of PCBs, where the electrical components are mounted on a single side of a board made of a conductive material, typically copper.
Multilayer PCBs have multiple layers of conductive material sandwiched between insulating layers, allowing for a higher density of components and more complex circuits.
Single-layer PCB
Double-layer PCB
Multi-layer PCB
Flexible PCB
Rigid PCB
Flex-rigid PCB
...










