Discover injection molding in this comprehensive guide. From the basic principles to the intricate machinery, this resource offers valuable insights and practical tips for beginners and seasoned professionals alike. Enhance your understanding and performance in injection molding for excellence. Buckle up for an enlightening experience!
What Is Injection Molding?
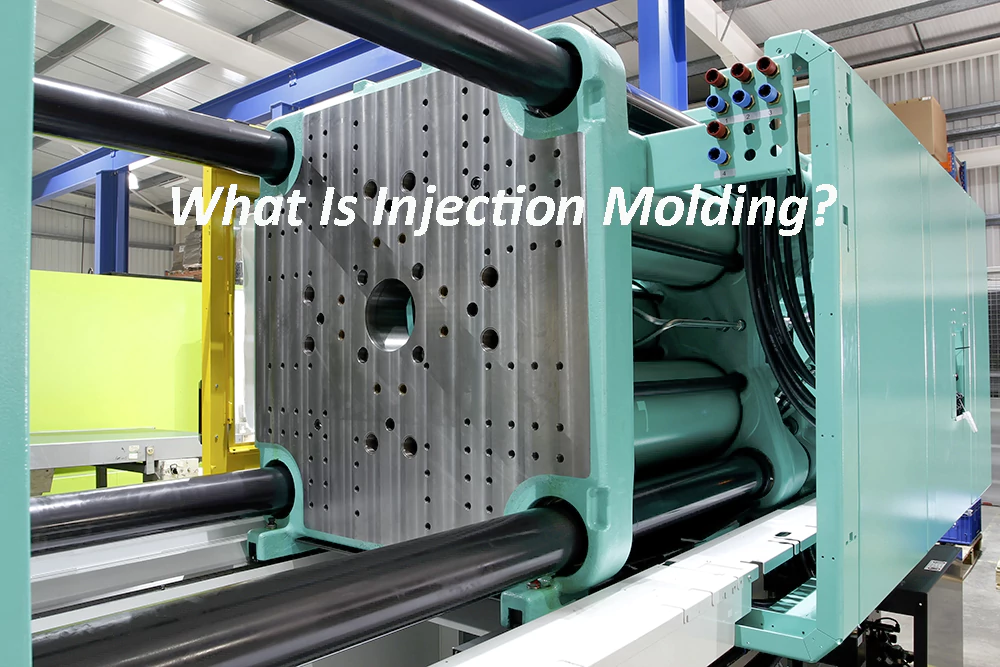
In manufacturing, injection molding is used in the production of materials via injection of molten material to form a mold. It is effective in the manufacture of a ton of items, including both large and small items.
Small items manufactured through injection molding include consumer goods, while larger items can include even automotive parts.
Injection molding is particularly ideal for high volumes of identical parts that requires consistency and high precision.
What Are Injection Molding Materials?
Materials used in injection molding include the following:
- Metal and ceramic powders such as metal alloys.
- Bioplastics such as starch-based plastics and polylactic acid.
- Engineering plastics such as polyethylene terephthalate, polycarbonate, and nylon (polyamide).
- Elastomers such as thermoplastic elastomers, polyurethane elastomers, and silicone.
- Thermosetting polymers such as polyurethane, phenolic, and epoxy.
- Thermoplastics such as acrylonitrile butadiene styrene, polystyrene, polyvinyl chloride, polypropylene, and polyethylene.
What Is Injection Molding Machine?
An injection molding machine is a device that produces molded plastic parts via an injection molding process. It converts raw plastic to the final shape of the desired item. Its main components include the following:
- Heating chamber or barrel.
- Hopper.
- Injection unit.
- Plunger or screw.
- Clamping unit.
- Mold.
- Cooling system.
- Ejection system.
- Control panel.
What Is The Principle Of Injection Molding?
The principle of injection molding focuses on the transformation of raw plastic material into complete products via a cyclic manufacturing procedure. These principles include the following:
1.Material preparation.
2.Melting.
3.Injection.
4.Cooling.
5.Mold opening.
6.Ejection.
7.Cycle repeat.
Principles of injection molding ensure that there’s a mass production of plastic parts. And at the same time, these principles ensure that there’s efficiency, consistency, and high precision.
Is 3D Printing Better Than Injection Molding?
When comparing injection molding to 3D printing, here are some of the factors to consider:
Production Volume
While injection molding is preferable for high-volume production, 3D printing is better for low and moderate production volumes.
Material Options
Materials used in 3D printing vary based on the printing technology and are limited. On the other hand, materials used in injection molding are limitless, including elastomers, plastics, and metals.
Part Complexity and Design Freedom
Injection molding is ideal for high-precision components and complex parts, and 3D printing is ideal for high design flexibility and the creation of sophisticated geometries. These may be expensive or challenging to achieve without the use of modern manufacturing.
Lead Time
3D printing has shorter lead times for both prototyping and low-volume production. It doesn’t require the creation of molds, which saves time. For injection molding, there are longer lead times because of mold creation.
Tooling Costs
3D printing has lower initial costs for setup due to the absence of molds. On the flip side, injection molding has higher initial costs for tools. However, in the long run, when dealing with bulk quantities, the initial costs are compensated in injection molding.
Surface Finish
Depending on the technology used in 3D printing, surface finish varies. Injection molding offers polished and smooth surface finishes. Unlike 3D printing, injection molding doesn’t present layer lines.
Waste Generation
Injection molding has fewer wastes as compared to 3D printing.
Material Properties
The material properties in 3D printing may be limited while injection molding has a wider range of materials.
Is It Cheaper To Injection Mold Or 3D Print?
Various factors will determine whether or not it is cheaper to use injection molding or 3D printing. They include:
Production Volume
When you have low to moderate production volumes, it is advisable to use 3D printing. On the contrary, if you have large production volumes, injection molding should be your choice.
Tooling Costs
Injection molding has higher tooling costs initially as compared to 3D printing.
Material Costs
For high-volume production, it would be cheaper to use injection molding materials.
Part Complexity
3D printing offers a higher design flexibility and the creation of complex geometries cost-effectively.
Post-Processing
Injection molding mostly needs less post-processing as compared to 3D printing, which cuts down on costs.
What Is Injection Molding Process?
The process involved in injection molding follows these steps:
1. Material selection.
2. Material preparation.
3. Melting.
4. Injection.
5. Cooling.
6. Mold opening.
7. Ejection.
8. Post-processing.
9. Cycle repeat.
How to Find an Injection Molding Manufacturer?
To find the right strategic partner to work with in injection molding, follow these steps:
1. Define your needs and requirements.
2. Conduct research online to evaluate manufacturers offering injection molding.
3. Check with relevant industry associations.
4. Attend industry exhibitions and trade shows.
5. Network.
6. Check different supplier directories to see relevant company offerings.
7. Request for quotations from the manufacturers that you identify.
8. Assess the capabilities of the manufacturers you shortlist to find the right target.
9. If you can, visit facilities in person and confirm how they manufacture.
10. Check references about the manufacturers.
11. Ensure there are relevant industry quality certifications in place.
12. Consider the cost that the manufacturer is quoting. Compare with different manufacturers. However, let this not be the main consideration. Also, consider quality.
13. Negotiate on terms and contracts before commencing work.
14. Commence with a pilot run and see how they perform, as you gain confidence working together.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, mastering precision is non-negotiable in achieving injection molding excellence. It involves meticulous planning, the right skill set, and the use of cutting-edge technology.
One company that stands at the forefront of this industry is IBE. With a relentless commitment to precision and quality, along with proven expertise in injection molding, IBE can help you navigate the complexities of this process. IBE is your go-to partner in your pursuit of injection molding excellence. Let’s transform your production processes with precision, together.
In manufacturing, injection molding is used in the production of materials via injection of molten material to form a mold. It is effective in the manufacture of a ton of items, including both large and small items.
Choosing between injection molding and 3D printing will depend on different factors. It is important to note that neither method is completely superior. Each method has its advantages and disadvantages. This uniqueness makes them specific to distinct applications across different industries. Therefore, in most cases, the choice of which is better will depend on your applications.
Various factors will determine whether or not it is cheaper to use injection molding or 3D printing. They include: Production Volume
When you have low to moderate production volumes, it is advisable to use 3D printing. On the contrary, if you have large production volumes, injection molding should be your choice.










