In the intricate world of electronics manufacturing, precision is paramount. Every tiny component, every minuscule connection plays a crucial role in determining the functionality and efficiency of the final product. Among the numerous tools and techniques employed in this field, the PCB stencil stands out as a quintessential instrument in ensuring accuracy and consistency throughout the manufacturing process.
What is a PCB stencil?
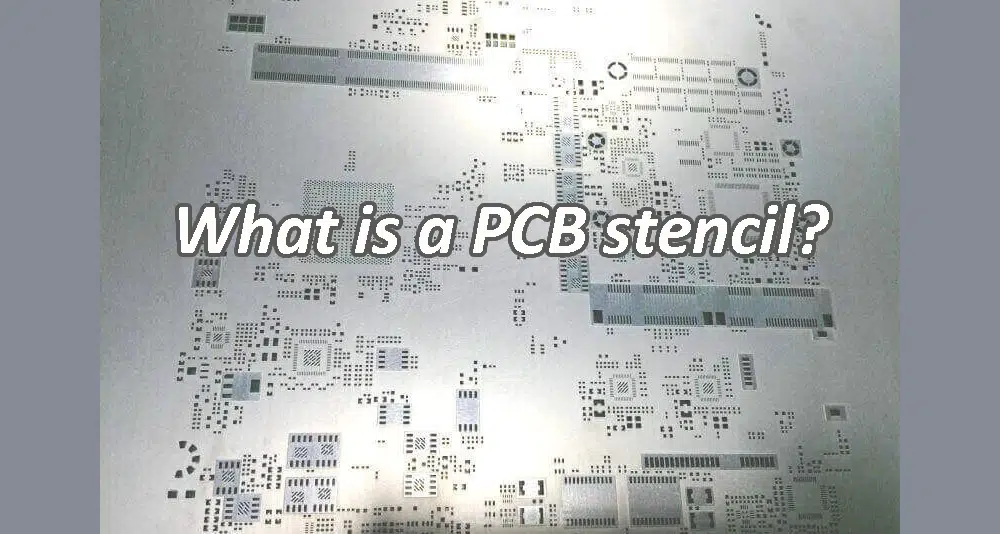
PCB stencils are commonly used in surface mount technology (SMT) assembly, where electronic components are mounted directly onto the surface of the PCB. Before placing the components, solder paste is applied to the solder pads through the stencil. The stencil ensures accurate and consistent application of solder paste, which is crucial for achieving proper solder joints during the reflow soldering process.
PCB stencils can be manufactured using various methods, including chemical etching, laser cutting, or electroforming. They come in different thicknesses and sizes, depending on the requirements of the PCB design and assembly process. Using a stencil can significantly improve efficiency and reliability in PCB assembly, especially for high-volume production.
What is the function of a PCB stencil?
The primary function of a PCB stencil is to facilitate the accurate and controlled application of solder paste onto the solder pads of a PCB during the assembly process. This is essential for surface mount technology (SMT) assembly, where electronic components are mounted directly onto the surface of the PCB.
Here’s a breakdown of its functions:
1. Solder Paste Application: The PCB stencil acts as a mask, allowing solder paste to be deposited onto specific areas of the PCB where components will be placed. The cutouts or openings in the stencil align precisely with the solder pads on the PCB, ensuring that the solder paste is applied only to those areas.
2. Accuracy and Consistency: By using a PCB stencil, manufacturers can achieve precise and consistent deposition of solder paste from one PCB to another. This consistency is crucial for ensuring the quality and reliability of solder joints across all assembled PCBs.
3. Minimizing Solder Bridging and Defects: Proper application of solder paste using a PCB stencil helps minimize the occurrence of solder bridging (where solder bridges form between adjacent pads) and other soldering defects. This is because the PCB stencil controls the amount and placement of solder paste, reducing the likelihood of excess solder causing shorts or other issues.
4. Improving Efficiency: Using a PCB stencil streamlines the solder paste application process, making it faster and more efficient compared to manual methods. This efficiency is particularly important in high-volume PCB assembly where consistency and speed are key factors.
In summary, the PCB stencil plays a crucial role in ensuring the accuracy, consistency, and reliability of solder paste application during the PCB assembly process, ultimately contributing to the overall quality of electronic products.
How to use PCB stencils?
Using a PCB stencil involves several steps, which typically include preparing the stencil, aligning it with the PCB, applying solder paste, and removing the PCB stencil. Here’s a general guide on how to use a PCB stencil:
1. Prepare the PCB Stencil:
– Ensure that the PCB stencil is clean and free from any debris or residues.
– Align the stencil with the corresponding solder pads on the PCB. PCB Stencils often have alignment features or fiducial marks to aid in proper positioning.
2. Secure the Stencil:
– Use tape, clamps, or a stencil holder to secure the PCB stencil in place over the PCB. Make sure it is firmly held down to prevent any movement during solder paste application.
3. Apply Solder Paste:
– Apply solder paste to one end of the stencil using a spatula, squeegee, or stencil printer. The solder paste should be evenly spread across the surface of the stencil.
4. Spread the Solder Paste:
– Using a squeegee or similar tool, spread the solder paste evenly across the PCB stencil surface, ensuring that it fills all the openings (apertures) in the PCB stencil.
5. Remove Excess Solder Paste:
– After spreading the solder paste, carefully remove any excess paste from the PCB stencil using the squeegee. This helps ensure that only the required amount of solder paste remains on the PCB.
6. Inspect the Solder Paste Application:
– Visually inspect the solder paste application to ensure that all solder pads are adequately covered and that there are no smudges, voids, or excess paste.
7. Remove the PCB Stencil:
– Once the solder paste application is complete and satisfactory, carefully lift the stencil from the PCB. Take care not to disturb the deposited solder paste.
8. Proceed with Component Placement:
– With the solder paste applied, proceed to place the surface mount components onto their respective solder pads on the PCB. Ensure proper alignment and orientation of the components.
9. Reflow Soldering:
– After component placement, the PCB is typically subjected to a reflow soldering process, where it is heated to melt the solder paste and create solder joints between the components and the PCB pads.
10. Inspect Solder Joints:
– After reflow soldering, visually inspect the solder joints to ensure they are properly formed and free from defects such as solder bridges or insufficient solder.
By following these steps, you can effectively use a PCB stencil to accurately apply solder paste during the PCB assembly process, helping to achieve high-quality and reliable solder joints.
What is stencil design in PCB?
PCB Stencil design involves creating a layout of the apertures on the stencil that correspond to the solder pads on the PCB. The size and shape of these apertures are crucial as they determine the amount and placement of solder paste deposited onto the pads.
The PCB stencil design process typically involves CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software, where engineers or designers create the stencil layout based on the PCB design. Factors such as component density, pad size, and pitch are considered during stencil design to ensure accurate solder paste deposition.
What materials are used in PCB stencils?

1. Stainless Steel:
– Stainless steel is one of the most widely used materials for PCB stencils due to its durability and resistance to corrosion. It is capable of withstanding multiple uses and can maintain its flatness over time. Stainless steel stencils are suitable for both laser cutting and chemical etching manufacturing methods.
2. Nickel:
– Nickel is another metal used for PCB stencils. It offers good durability and is suitable for electroforming, a manufacturing method where metal is deposited onto a patterned substrate through an electroplating process. Nickel stencils are known for their high precision and smooth aperture walls.
3. Polyester Film (Mylar):
– Polyester film, commonly known as Mylar, is a flexible polymer material used for making low-cost PCB stencils. Mylar stencils are typically used for prototyping or low-volume production. They are manufactured using a laser cutting process and are suitable for single-use applications.
4. Polyimide Film (Kapton):
– Polyimide film, often referred to as Kapton, is another flexible polymer material used for making PCB stencils. Kapton stencils offer higher temperature resistance compared to Mylar stencils, making them suitable for reflow soldering processes with elevated temperatures. They are also manufactured using laser cutting and are suitable for single-use applications.
5. Brass:
– Brass stencils are less common but can be used for certain applications. Brass offers good durability and can be manufactured using chemical etching methods. Brass stencils are often used for thicker stencil requirements or special applications where the properties of brass are advantageous.
Each material has its advantages and limitations, and the choice depends on factors such as the specific requirements of the PCB assembly process, budget constraints, and manufacturing capabilities.
How to clean PCB stencil?
Cleaning a PCB stencil is important to ensure the quality and accuracy of solder paste application during PCB assembly. Here’s a general guide on how to clean a PCB stencil:
Remove Excess Solder Paste:
After using the stencil for solder paste application, immediately remove any excess solder paste from both sides of the PCB stencil using a spatula or scraper. This helps prevent dried solder paste from hardening on the stencil.
Use Solvent Cleaner:
Apply a solvent cleaner specifically designed for removing solder paste to the PCB stencil. Isopropyl alcohol (IPA) is commonly used for this purpose. Use a lint-free cloth or stencil cleaning wipes saturated with solvent to wipe both sides of the stencil thoroughly.
Scrubbing and Brushing:
For stubborn residues or dried solder paste, gently scrub the PCB stencil using a soft-bristled brush or a stencil cleaning brush. Be careful not to damage the stencil material or the aperture walls during scrubbing.
Rinse with Clean Solvent:
After scrubbing, rinse the stencil with clean solvent to remove any remaining residues. Ensure that the solvent completely evaporates to prevent contamination during future use.
Inspect for Residues:
Visually inspect the PCB stencil to ensure that all residues and contaminants have been removed. Pay close attention to the aperture walls and corners, as residues in these areas can affect solder paste transfer during the next use.
Dry Thoroughly:
Allow the PCB stencil to air dry completely before storing or using it again. Ensure that there is no moisture remaining on the stencil, as moisture can lead to oxidation and corrosion of metal stencils.
Store Properly:
Store the cleaned and dried stencil in a clean and dry environment to prevent contamination. Avoid bending or folding the PCB stencil, as this can affect its flatness and accuracy.
Regular Maintenance:
Implement a regular cleaning and maintenance schedule for the PCB stencil to prevent the buildup of residues and ensure consistent solder paste application quality.
What is the best thickness for PCB stencils?
The best thickness for a PCB stencil depends on various factors including the specific application, the type of components being assembled, and the requirements of the solder paste printing process. However, a common thickness range for PCB stencils is typically between 0.1 mm to 0.25 mm (or 4 to 10 mils).
What size is a PCB stencil?
PCB stencils are typically sized to match the dimensions of the PCB they are designed for, with some additional margin for alignment and handling. The size of the stencil is usually slightly larger than the PCB itself to ensure adequate coverage of all solder pads and components.
Common sizes for PCB stencils are based on industry-standard frame sizes, such as:
Standard Frame Sizes: Common frame sizes for PCB stencils include 23″ x 23″ (584 mm x 584 mm), 29″ x 29″ (737 mm x 737 mm), and 29″ x 29″ (737 mm x 737 mm). These sizes accommodate various PCB dimensions and are compatible with most stencil printers and assembly equipment.
Custom Sizes: In addition to standard frame sizes, PCB stencils can also be custom-made to match the specific dimensions and requirements of the PCB layout. Custom-sized stencils may be necessary for PCBs with non-standard dimensions, complex designs, or specialized applications.
Stencil Thickness: The thickness of the stencil material (typically stainless steel) is also an important factor to consider. Common thicknesses range from 0.1 mm to 0.25 mm (4 mils to 10 mils), depending on the application and solder paste printing requirements.

What is the framework for a PCB stencil?
The framework for a PCB stencil refers to the supporting structure that holds the stencil in place during the solder paste printing process. This framework, often referred to as a stencil frame or stencil holder, provides stability and alignment for the stencil, ensuring accurate and consistent solder paste deposition onto the PCB.
Conclusion
From facilitating precise solder paste application to enabling alignment and registration of components, stencils are indispensable tools for achieving high-quality PCB assemblies. As technology continues to evolve and electronic devices become increasingly sophisticated, the importance of PCB stencils in enabling reliable and cost-effective manufacturing processes is only set to grow.
A PCB stencil is a thin sheet of material, typically metal (such as stainless steel), with precise cutouts or openings that correspond to the solder pads on a printed circuit board (PCB).
Solder Paste Application
Accuracy and Consistency
Minimizing Solder Bridging and Defects
Improving Efficiency
Stainless Steel
Nickel
Polyester Film (Mylar)
Polyimide Film (Kapton)
Brass










