With the rapid development of technology, chips have become the core of modern electronic equipment. They not only control and operate various equipment, but also determine the performance and function of these equipment. This article will introduce you to the different types of chips, their characteristics and applications.
A semiconductor chip, also known as an integrated circuit or microprocessor, is a tiny electronic device that integrates a large number of electronic components (such as transistors, resistors, capacitors, etc.) on a small silicon chip. According to functions, uses, processes, principles, etc., the classification of chips can be described as diverse, varied, and messy. Today’s article will introduce the classification of chips:
Classified by function
According to the function, semiconductor chips are divided into five categories: logic chips, memory chips, sensor chips, power chips and communication chips. Each major category can be subdivided into several subcategories.
logic chip
Serial processing chip: CPU
Parallel processing chip: GPU
Programmable logic devices: FPGA, CPLD
Customized special purpose chip:ASIC
Including: PMU, NPU, DPU, MCU, etc.
Communication chip
Cellular communication chip: 2G, 3G, 4G, 5G
Near field communication chips: Bluetooth, WiFi, NFC, etc.
Satellite communication chip
Interface communication chip: HDMI, VGA, etc.
Sensor chip
Image sensor chip: CIS
Micro Electro Mechanical System Chip: MEMS
Touch chip, audio chip, GPS chip
chips, Hall sensor chips, etc.
Power chip
DCDC, ACDC power chip
LDO linear voltage regulator chip
power management chip
Memory chip
Flash:CPU
Read-only memory: ROM
Random access memory: SRAM, DRAM
Classified by working principle
According to the working principle, semiconductor chips can be divided into two categories: analog chips and digital chips.
Analog chips: Analog chips process natural analog signals such as continuous light, sound, speed, and temperature (including radio frequency chips, sensor chips, etc.). Generally, the process requirements for chips are not high (especially for high-power devices, sometimes the substrate is more expensive than the process), and more attention is paid to the characteristics of components such as reliability, stability, energy conversion efficiency, voltage and current control capabilities, etc.
Digital chip: The main function of digital chip is to realize digital information transmission. The basic functions of digital include storage, calculation, operation, etc. Its performance directly depends on the number of transistors per unit area and is therefore very dependent on the process.
Classified by application
Data center-level chips: Mainly used in cloud computing data centers: including CPU, GPU, memory, storage controller, solid-state drive, etc., which mainly require high performance, high stability, and high reliability.
Consumer chips: Currently the most widely used chips with the highest market share, used in computers, mobile phones and other products.
Industrial chips: Industrial products have been exposed to harsh environments of extremely high/low temperature, high humidity, strong salt spray and electromagnetic radiation for a long time. The use environment is harsh. Therefore, industrial chips must have stability, high reliability and high safety, and have long service life.
Automotive grade chips: mainly because they have strict requirements on the temperature environment and can be used in a wider temperature range.
Military chips: Semiconductor chips related to national defense and military industries, such as satellite communications, guidance, and precision navigation.
Classified by technology
1971,10μm process
1974,6μm process
1977,3μm process
1982,1.5μm process
1984,ASML found。
1985,1μm process
1989,0.8μm process
1994,0.6μm process
1995,0.35μm process
1997:250nm process
1999:180nm process
2001:130nm process
In 2003, ASML cooperated with TSMC to launch an immersion lithography machine, and ASML has surpassed other manufacturers in one fell swoop. The 157nm light source dry lithography machines promoted by Japan’s Nikon and Japan’s Canon, both lithography giants, were gradually abandoned by the market, and the two companies turned from prosperity to decline.
2004:90nm process
2006:65nm process
2008:45nm process
2010:32nm process
2011:22nm process
In 2013, ASML launched the first EUV mass-produced product, and NXE:3300 was officially shipped, further strengthening the monopoly position in the industry.
2014:14nm process
2017:10nm process
2018:7nm process
2020:5nm process
2022:3nm process
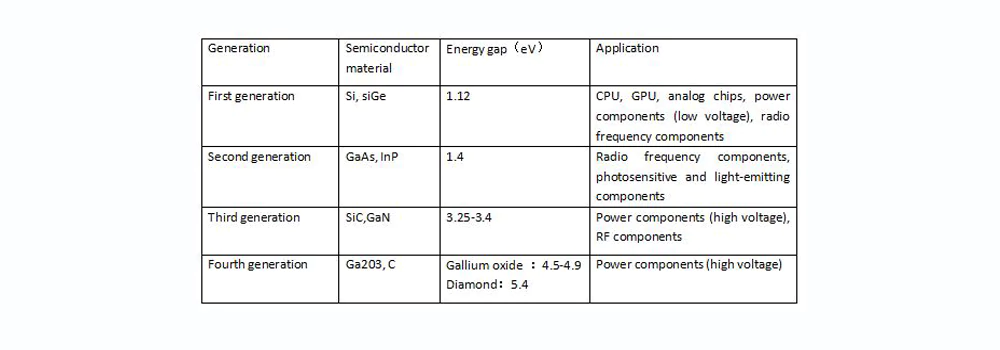
Classified by semiconductor material
Classified by industrial chain
According to the order of the integrated circuit industry, semiconductor chips include five major processes: silicon wafer production, IC design, wafer manufacturing, packaging and testing.
Semiconductor chip manufacturing can be divided into front-end process and back-end process. Front-end processes include photolithography, etching, thin film deposition, ion implantation, cleaning, chemical mechanical polishing, measurement and other processes. The back-end processes include thinning, dicing, chip mounting, bonding and other packaging processes as well as terminal testing.











